Ethereum activated the Fusaka improve on December 3, 2025 to enhance the community’s knowledge availability capability via BLOB parameter overrides that incrementally broaden BLOB targets and maximums.
Two subsequent changes raised the aim from 6 blobs per block to 10 to 14, bringing the utmost cap to 21. The aim was to cut back layer 2 rollup prices by rising the throughput of BLOB knowledge, that are compressed transaction bundles the place rollups are posted to Ethereum for safety and finality.
After three months of information assortment, it grew to become clear that there was a spot between capability and utilization. Since Fusaka’s activation, MigaLabs has analyzed greater than 750,000 slots and located that the community has fallen wanting the goal variety of 14 blobs.
After the primary parameter adjustment, the median BLOB utilization really decreased, and the miss charge elevated for blocks containing 16 or extra BLOBs, suggesting decreased reliability on the fringe of the brand new capability.
The conclusion of the report is simple: don’t enhance blob parameters any additional till excessive blob miss charges normalize and the demand for headroom that has already been created materializes.
What did Fusaka change and when did it occur?
Ethereum’s pre-Fusaka baseline, established via EIP-7691, focused 6 BLOBs per block, with a most of 9 BLOBs. The Fusaka improve launched two consecutive BLOB parameter override changes.
The primary one was activated on December ninth and raised the goal to 10 and the utmost to fifteen. The second was activated on January 7, 2026, rising the goal to 14 and the utmost to 21.
These modifications don’t require a tough fork, and this mechanism permits Ethereum to dial in capability via shopper changes reasonably than protocol-level upgrades.
MigaLabs evaluation, which printed reproducible code and methodology, tracked blob utilization and community efficiency all through this migration.
The outcomes confirmed that although the community capability elevated, the median variety of blobs per block decreased from 6 earlier than the primary override to 4 after. Blocks containing 16 or extra blobs are nonetheless very uncommon, occurring between 165 and 259 instances over your complete statement window, relying on the precise variety of blobs.
The community has unused headroom.
There’s one parameter battle. The report’s timeline textual content describes the primary override as rising the aim from 6 to 12, whereas the Ethereum Basis’s mainnet announcement and shopper documentation describe the adjustment as 6 to 10.
Makes use of Ethereum Basis parameters as a supply. Baseline is 6/9, 10/15 after first override, 14/21 after second override. However, we deal with the dataset of reviews on noticed utilization and miss charge patterns as our empirical spine.
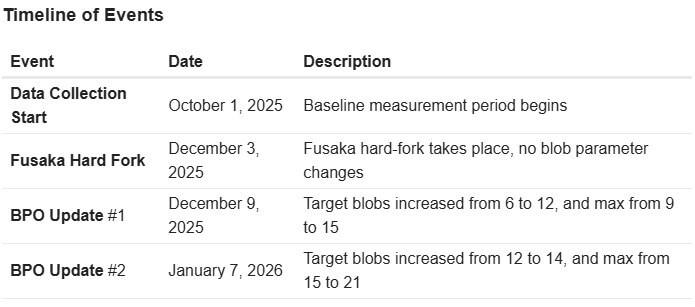
The upper the variety of blobs, the upper the miss charge.
Community reliability measured via lacking slots, that are blocks that can not be propagated or verified appropriately, reveals a transparent sample.
For low blob counts, the baseline miss charge is roughly 0.5%. When the block reaches 16 or extra blobs, the miss charge will increase from 0.77% to 1.79%. On the most capability of 21 blobs launched within the second override, the miss charge reaches 1.79%, greater than thrice greater than the baseline.
The evaluation categorizes this into blob numbers from 10 to 21 and reveals a gradual degradation curve that accelerates when the blob goal worth of 14 is exceeded.
This drop is necessary as a result of it means that the community infrastructure, resembling validator {hardware}, community bandwidth, and authentication timing, is struggling to deal with blocks which have reached their capability.
As demand finally will increase to fulfill the 14 blob aim or method as much as 21 blobs, the elevated miss charge can result in vital finality delays and reorganization dangers. The report summarizes this as a stability boundary. Though the community can technically deal with excessive blob blocks, whether or not it does so constantly and reliably stays an open query.
Blob Economics: Why the bottom value ground issues
Mr. Fusaka has not solely expanded manufacturing capability. Blob pricing was additionally modified via EIP-7918, introducing a ground value to stop blob auctions from collapsing to one-way.
Previous to this variation, if execution prices prevailed and demand for blobs remained low, the bottom value for blobs may drop till they successfully disappeared as a value sign. Layer 2 rollups pay blob charges to put up transaction knowledge to Ethereum. These charges are believed to mirror the computational and community prices that BLOB imposes.
When costs drop to close zero, the financial suggestions loop breaks and rollups devour capability with out paying proportionately. Because of this, the community loses monitor of precise demand.
EIP-7918’s ground value ties blob charges to execution prices, guaranteeing that value stays a significant sign even when demand is low.
This prevents the free rider downside the place low cost blobs encourage wasteful utilization and supplies clearer knowledge for future capability selections. If blob costs stay excessive regardless of elevated capability, then demand is actual. In case you fall to the ground, headroom exists.
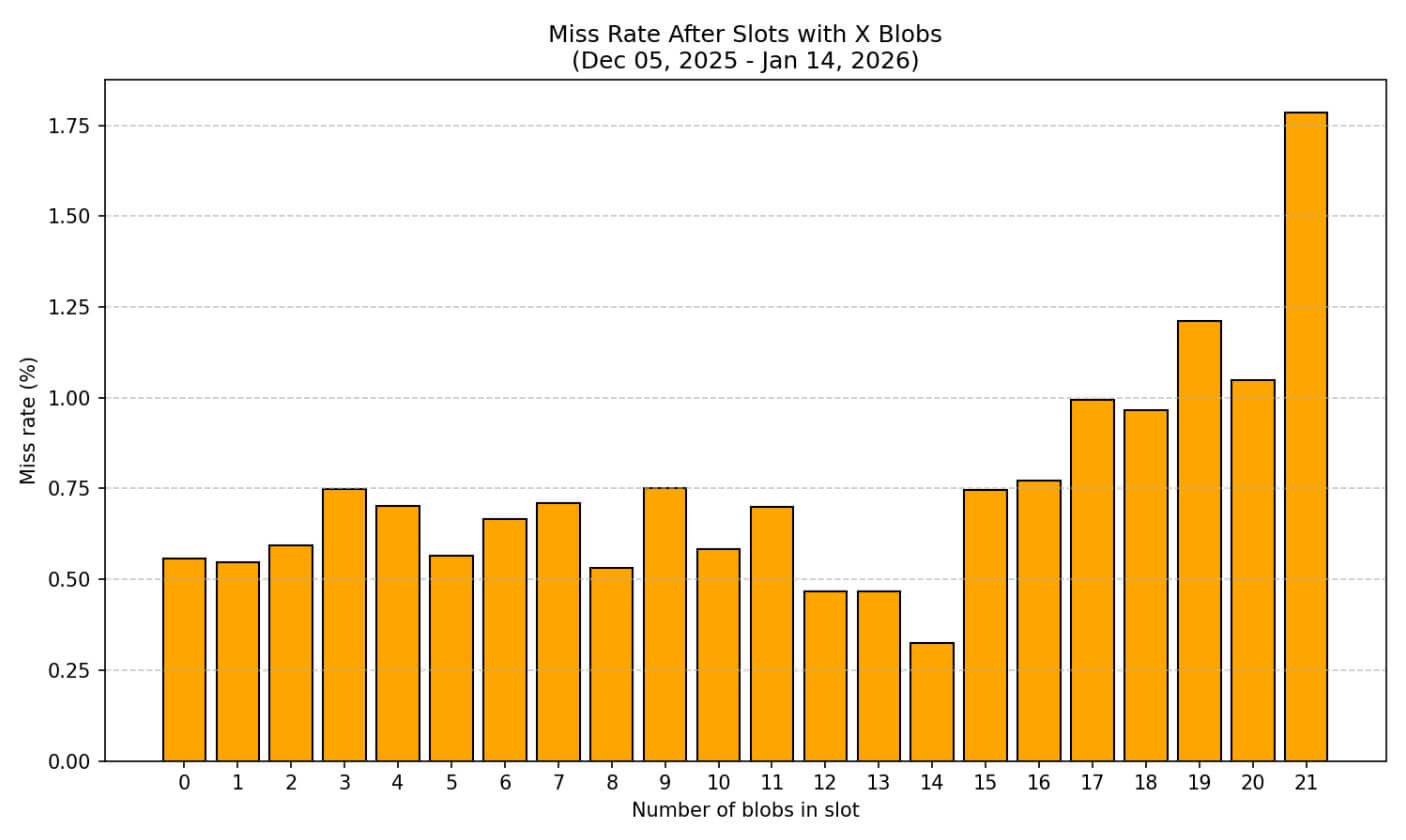
Early knowledge from Hildobby’s Dune dashboard, which tracks Ethereum blobs, reveals that blob charges have stabilized since Fusaka, reasonably than persevering with the downward spiral seen earlier.
The typical variety of blobs per block confirms MigaLabs’ findings that utilization has not spiked sufficient to fill new capability. Blocks usually comprise fewer than the 14 blob goal, and the distribution stays closely skewed towards decrease counts.
What the information reveals about effectiveness
Fusaka has efficiently expanded its technical capabilities and confirmed that the Blob parameter override mechanism works with out the necessity for a controversial exhausting fork.
The minimal value ground seems to be working as meant, stopping blob charges from turning into economically meaningless. Nonetheless, utilization lags behind capability, and new capability is turning into much less dependable on the edge.
The miss charge curve means that Ethereum’s present infrastructure comfortably handles the ten/15 parameters of the pre-Fusaka baseline and the primary override, however begins to pressure past 16 blobs.
This creates a threat profile. As layer 2 exercise spikes and blocks often method ~21 blobs, the community can face elevated miss charges that compromise finality and reorganization tolerance.
Demand patterns present one other sign. Regardless of the rise in capability, the median blob utilization drops after the primary override, suggesting that Layer 2 rollups will not be presently constrained by blob availability.
Both your transaction quantity will not be massive sufficient to require many blobs per block, or you might be optimizing compression and batching to suit inside present capability reasonably than increasing utilization.
Blobscan, a devoted blob explorer, reveals particular person rollups posting comparatively constant blob counts over time, reasonably than rising to make the most of new headroom.
Previous to Fusaka, the priority was that restricted blob capability would change into a bottleneck for layer 2 scaling and rollup fees would proceed to rise because the community competed for the provision of scarce knowledge. Fusaka talked about capability constraints, however the bottleneck seems to be altering.
The rollup will not be filling the out there house. Which means demand has not arrived but, or different elements resembling sequencer economics, consumer exercise, and fragmentation between rollups are limiting development greater than blob availability.
what occurs subsequent
Ethereum’s roadmap consists of PeerDAS, a extra basic redesign of information availability sampling that additional expands blob capability whereas bettering decentralization and safety properties.
Nonetheless, Fusaka’s outcomes recommend that uncooked capability will not be a binding constraint at the moment.
The community has room to develop to 14/21 parameters earlier than additional enlargement is required, and a reliability curve with a excessive blob depend signifies that infrastructure upgrades could must catch up earlier than capability will increase once more.
Miss charge knowledge present clear boundary circumstances. If Ethereum pushes capability, although the miss charge stays excessive for 16+ blob blocks, there’s a threat of system instability that would floor in periods of excessive demand.
A safer method is to extend utilization towards the present aim, monitor whether or not the miss charge improves as purchasers optimize for greater blob hundreds, and modify parameters solely when the community reveals that it may reliably deal with edge circumstances.
The effectiveness of Fusaka is dependent upon the symptoms. We efficiently expanded capability and stabilized BLOB costs via a reserve ground. It didn’t instantly enhance utilization or remedy reliability points at full capability.
This improve has created room for future development, however whether or not that development will materialize is an open query that the information doesn’t but reply.


