Layer 2 blockchain is a vital a part of the Ethereum ecosystem. These are constructed to onboard new customers and allow mass adoption of blockchain expertise. However how does Layer 2 blockchain make this attainable? And why are transactions cheaper and sooner in L2? On this information, we’ll let you know all about Layer 2 scaling options.
What’s layer 2 of blockchain?
Layer 2 definition
A Layer 2 community is a secondary blockchain that exists inside one other community generally known as Layer 1. It processes and executes transactions from the principle chain and sends the outcomes to the layer 1 chain.
Layer 2 blockchain can also be known as a layer 2 answer as a result of it solves the scalability drawback.
Why blockchain wants a layer 2 answer
Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum have scalability limitations. To course of extra transactions per second (TPS) and scale back fuel charges, you want a layer 2 blockchain.
It’ll additionally speed up the adoption of cryptocurrencies and decentralized apps (dApps).
Relationship between layer 1 and layer 2
Layer 1 is the essential chain that gives safety and consensus. Layer 2 processes 1000’s of transactions shortly and cheaply, however nonetheless depends on the Layer 1 blockchain to confirm and finalize every part.
How does Layer 2 work?
Off-chain processing and on-chain funds
Layer 2 blockchain is appropriate with Ethereum. Customers can ship and obtain tokens and work together with good contracts on the tokens. L2 is extremely scalable as a result of it makes use of a distinct mechanism to calculate and course of transactions off-chain.
L2 then bundles the transactions and sends them to the bottom layer. This step varies relying on the kind of Layer 2 answer getting used. Some options ship cryptographic proofs to the bottom layer. You might also assume that each one transactions are legitimate.
Lastly, L2 sends the information to L1 by way of the good contract. The bottom layer resolves any disputes and provides legitimate transactions to the subsequent block.
Safety inherited from the bottom layer
Layer 2 options inherit safety from Ethereum. Such options have good contracts deployed at layer 1. The opposite L2 depends on the bridge to speak. The good contract receives the ultimate steadiness and the state of the L2 community. The bottom layer then validates the submitted knowledge by way of attestation or problem mechanisms.
As a result of Layer 2 transactions happen off-chain, Ethereum’s consensus mechanism and immutability make it the last word supply of fact. Any proof of wrongdoing, proof of validity, or nationwide dedication submitted by the L2 community is lastly finalized on the base layer. This reduces malicious conduct that happens on the L2 community.
Transaction pace and value discount
Transactions on L2 networks are quick and low-cost. Such secondary networks are nice for frequent merchants. Transactions on the Layer 2 community undergo a sequencer, so they’re processed sooner. A sequencer is a server or cluster of servers that processes transactions. They are often centralized or decentralized and operated by people, firms, or third-party operators.
Transactions in L2 networks are low-cost as a result of the sequencer bundles transactions and sends them as a single transaction to the bottom layer. This strategy considerably reduces fuel fees by splitting the fuel fees for a single baselayer transaction amongst L2 customers.
Layer 2 answer sorts
Rollup (optimistic rollup, ZK rollup)
Rollups are a technique to bundle tons of of transactions on a Layer 2 community right into a single transaction on Layer 1. There are two forms of L2 rollups:
- optimistic rollup
- Zero-knowledge proof (ZK) rollup.
Each sorts bundle layer 2 transactions, however work together with the bottom layer in a different way.
optimistic rollup
Optimistic rollups carry out transactions off-chain and ship knowledge to the bottom layer by way of calldata or blobs. This strategy assumes that each one transactions are legitimate, therefore the title. Optimistic Rollup compresses transaction knowledge earlier than sending it to Ethereum to cut back prices.
As soon as an Ethereum good contract receives transaction knowledge, anybody can problem this optimistic assumption utilizing proof of fraud inside a sure dispute interval. Ethereum primarily takes an “harmless till confirmed responsible” strategy when coping with optimistic rollups.
This battle window varies relying on the Layer 2 answer. And people who problem this assumption are Ethereum individuals generally known as validators or watchers.
Upon profitable proof of fraud, Ethereum reverts to an invalid state and malicious sequencers are penalized by dropping their staked ETH collateral. The proper state is then utilized to the bottom layer.
If legitimate proof of fraud isn’t supplied throughout the dispute interval, the sequence of transactions can be deemed legitimate and finalized on Ethereum.
ZK roll up
Zero-knowledge proof rollups (ZK rollups) work equally to optimistic rollups. They execute 1000’s of transactions off-chain and ship knowledge to good contracts that reside on the bottom layer. Nonetheless, fairly than assuming that each one transactions are legitimate, ZK-Rollups proves that each one transactions are legitimate earlier than sending them to Ethereum. That is completed by producing a cryptographic proof, also called a zero-knowledge proof, that mathematically verifies the correctness of all the batch.
ZK Rollup depends on operators (aka provers or sequencers) to course of transactions, generate proofs, and ship them to Ethereum. Some rollups depend on centralized operators, whereas others use semi-distributed provers. Proof is verified immediately, so there isn’t any dispute interval and customers can entry their funds instantly. As soon as the proof of validity is accepted by the Ethereum good contract, the transaction knowledge is added to the subsequent verified block on the bottom layer.
state channel
State channels are one other technique to prolong Ethereum. A single state channel permits two or extra individuals to ship and obtain tokens shortly and cheaply, with out on-chain funds. As soon as the transaction is completed, the ultimate state and transaction abstract will be despatched to Ethereum.
State channels are peer-to-peer (p2p) and managed by multi-signature good contracts. To open a state channel, friends should lock funds into good contracts constructed on high of the bottom layer. Locked funds are collateral to make sure integrity and stop disputes. All state modifications are carried out and verified by their friends. This strategy reduces fuel charges, calculations on Ethereum, and hurries up transactions.
Within the occasion of a dispute between individuals, the problem is resolved on the base layer and Ethereum consensus enforces the newest signature state.
State channels have some limitations. Friends should keep on-line and monitor the channel always. It is usually not user-friendly and troublesome to watch a number of channels on the similar time.
plasma chain
The plasma chain is a separate chain linked to the bottom layer, on this case known as the foundation chain or father or mother chain. Plasma chains, also called youngster chains, are managed by good contracts deployed on the father or mother chain.
Plasma Chain processes and verifies transactions off-chain, lowering the verification load on Ethereum. Transactions are sooner as a result of they depend on a number of operators to prepare and execute them. Nonetheless, solely the ultimate state is periodically despatched to Ethereum for safety anchoring.
To make the most of Plasma Chain, customers should deposit Ether or ERC-20 tokens into a wise contract. The operator will create new tokens equal to the person’s funds. To exit Plasma Chain, you have to submit a withdrawal request. Your request will then be disputed by way of our fraud prevention options for roughly 7 days. If the problem fails, your withdrawal request can be permitted and executed. Nonetheless, if the problem is profitable, the operator can be penalized.
Plasma chains seem to work like rollups, however with some limitations. The lengthy exit queue from Plasma Chain to Ethereum faces a big drawback of knowledge unavailability. It is because the Plasma Chain operator shops the information and sends it to Ethereum solely periodically. Rollup, then again, gives full transaction knowledge each time a person needs to commerce or withdraw funds.
Sidechain (and why it is completely different from true L2)
Sidechains are usually not layer 2 networks. Nonetheless, they may help scale up Ethereum. These are separate blockchains that connect with Ethereum by way of a bridge. Sidechains have completely different block specs and consensus mechanisms. They don’t inherit Ethereum’s safety properties and don’t put up transaction knowledge or state routes to Ethereum. This makes malicious assaults and centralization extra seemingly.
To realize excessive throughput, sidechains implement bigger block sizes and better fuel limits. Highly effective {hardware} is required to run bigger blocks with quick processing instances. This makes it troublesome for everybody to run a full node, resulting in centralization and malicious assaults.
The sidechain is EVM appropriate and permits you to run Ethereum dApps with minimal modifications. Sidechains work together with Ethereum by way of bridges, that are collections of good contracts deployed on each chains. This bridge implements a mint and burn mechanism that permits customers to enter sidechains, commerce, and return to Ethereum.
Fashionable Layer 2 Initiatives in 2025
determination
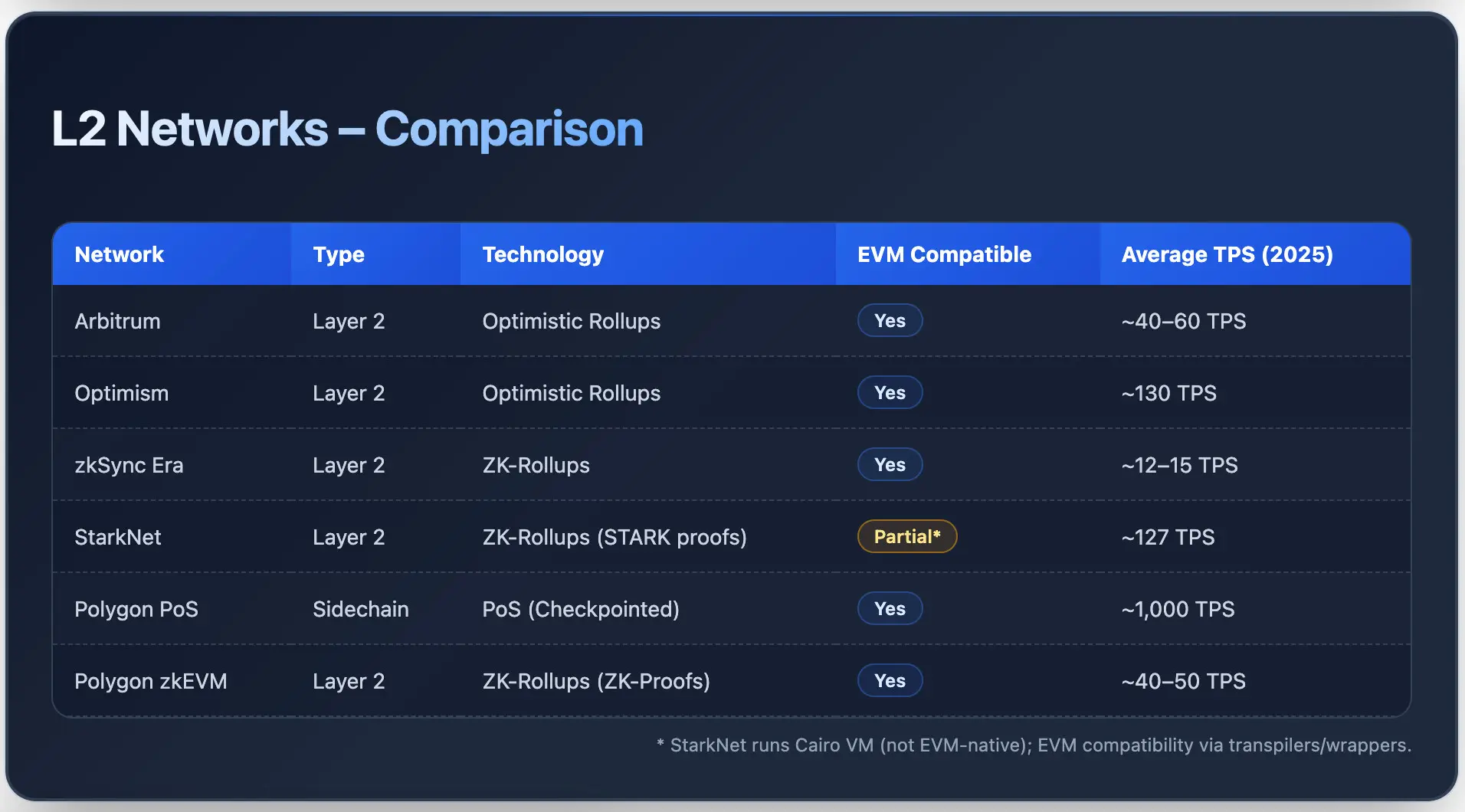
Arbitrum is an L2 that makes use of Optimistic Rollups to course of transactions off-chain and put up them to Ethereum. It provides merchants low charges whereas counting on the safety of Ethereum.
Arbitrum helps Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM), permitting builders to simply deploy good contracts with minimal modifications. L2 has a set of merchandise serving DeFi, gaming, and enterprise dApps, together with Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, and Arbitrum Orbit.
The common fuel value per transaction in June 2025 ranged from $0.007 to $0.015. It prices a median of $0.30 to trade a token, and transactions are accomplished inside minutes.
optimism
Optimism is an Ethereum-compatible L2 that depends on Optimistic Rollups. Just like Arbitrum, Optimism executes transactions off-chain and sends bundled knowledge to Ethereum. L2 provides decrease fuel costs and better TPS charges.
Optimism is constructed with a modular OP stack, permitting builders to simply deploy EVM good contracts. As of 2025, Optimism Superchain has processed 2.47 billion transactions and secured roughly $3.4 billion in complete worth locked (TVL). The common block time of the community is 200ms.
zkSync period
zkSync Period is a layer 2 scaling answer for Ethereum and makes use of ZK rollups. This works in an identical technique to Optimism and Arbitrum. Nonetheless, this one is completely different and makes use of ZK rollup expertise. zkSync processes transactions off-chain and proves their validity earlier than sending them to Ethereum.
The common buying and selling quantity per day is zkSync It grew from 290,000 in This fall 2024 to 1.1 million in Q1 2025. Common charges additionally fell to $0.03 per commerce in Q1 2025. Based mostly on knowledge collected from zkSync blockchain explorerthe community processed roughly 465 million transactions, with a median block time of 2-4 seconds.
stark internet
StarkNet is an L2 that makes use of ZK rollups, or validity rollups, constructed on high of Ethereum. L2 makes use of STARK proofs to make sure that all off-chain transaction bundles are verified earlier than settlement on the base layer.
In mid-2025, StarkNet reached Stage 1 decentralization, a milestone within the rollup community framework proposed by Vitalik Buterin. Which means that the StarkNet rollup has crossed key technical and governance thresholds, bringing the community nearer to full decentralization.
StarkNet helps Cairo-based good contracts and native account abstraction. The common buying and selling price on StarkNet may be very low, round $0.0013. The community recorded over 127 TPS in late 2024 with affirmation instances of lower than 2 seconds.
Polygon PoS and Polygon zkEVM
Polygon PoS is a high-throughput sidechain. It’s EVM appropriate and helps scale Ethereum. Sidechains use a dual-layer structure and course of transactions from the bottom chain. There are common checkpoints to make sure funds and safety on Ethereum. Polygon PoS has a transaction throughput of roughly 1,000 TPS and helps tens of millions of customers with fuel charges of lower than $0.01.
Polygon zkEVM is an L2 community. It’s totally appropriate with EVM and makes use of ZK-Proofs to validate transactions earlier than posting them to Ethereum. As of 2025, Polygon zkEVM will course of roughly 40-50 TPS, with peak capability reaching over 200 TPS throughout testing. Common fuel charges vary from $0.02 to $0.05 per transaction, which is about 90% cheaper in comparison with Ethereum.
Benefits of Layer 2 Blockchain
Decreased transaction charges
One of many predominant benefits of layer 2 blockchains is low transaction charges. In the course of the 2021 bull market, Ethereum charged customers tons of and even 1000’s of {dollars} on account of community congestion. Layer 2 networks clear up this drawback by bundling transactions and splitting the price of a single Ethereum transaction amongst many customers, minimizing charges.
sooner transaction speeds
Layer 2 networks present near-instantaneous transactions as a result of they depend on sequencers to shortly order and course of transactions. Alternatively, Ethereum is a decentralized validator community, so it takes time to substantiate transactions.
DeFi, NFT, and gaming scalability
Layer 2 blockchain gives a perfect playground for DeFi, NFTs, and gaming dApps to develop and acquire mass adoption. Transaction charges are negligible, so sending and receiving cash, in-game gadgets, and different forms of NFTs is simple and practically instantaneous.
Improved person expertise
L2 networks present a greater person expertise, particularly for brand spanking new customers. These scale back latency, scale back entry prices, and simplify interactions with dApps. Customers profit from near-instantaneous transactions and easy entry to dApps with out experiencing congestion in comparison with the bottom layer.
Layer 2 challenges and dangers
Safety conditions
Layer 2 networks inherit safety from Ethereum, however introduce their very own belief assumptions. Sequencers, bridges, and knowledge availability layers will be vital factors of failure. If invalid knowledge is submitted or the proof problem fails, operators could lose their ETH stake and customers could lose funds or expertise delays.
Bridging person expertise and danger
Shifting tokens between L1 and L2 or vice versa includes some dangers. Complicated UX or poor pockets integration may cause customers to lose funds or expertise delays, driving them away regardless of low charges and excessive throughput.
Issues about centralization
L2 networks are technically centralized, as they depend on sequencers operated by chosen validators. This could result in censorship, downtime, and technical failures, lowering decentralization and person belief.
Regulatory uncertainty
L2 networks function in a grey zone. Establishments are usually not at the moment adopting L2 networks on account of unclear guidelines relating to storage, coin classification, and infrastructure.
Layer 2 vs. Layer 1: Key Variations
Cost and safety
Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks function in a different way by way of funds and safety. L1 instantly settles transactions, whereas L2 depends on the bottom chain settlement layer. Whereas L1 has full safety by way of a consensus mechanism and a community of validators, L2’s safety depends on Layer 1.
Pace and throughput
Layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains have completely different speeds and throughput charges. Just like Ethereum, L1 is proscribed to some dozen transactions per second (roughly 10-15 TPS).
As a result of L2 networks course of transactions off-chain, they deal with tons of or 1000’s of TPS.
Mainly, L2 is quicker than L1, making it preferrred for real-time interactions with customers and dApps.
Use circumstances and tradeoffs
L1 is right for high-value transactions the place decentralization is essential. For instance, Ethereum is utilized by stablecoin issuers and institutional DeFi platforms comparable to Aave. L1 can also be nice for transferring NFTs like CryptoPunks and Pudgy Penguins since they’re costly gadgets.
L2 is right for frequent, low-fee transactions comparable to microtransactions, gaming, and high-frequency buying and selling. The tradeoff of L2 is quicker and cheaper transactions, however much less centralization and safety.
The way forward for layer 2 scaling
Ethereum rollup-centered roadmap
Ethereum’s roadmap contains Dank Sharding and Protodunk Sharding.
In EIP-4844, protodunk sharding brings low-cost BLOB knowledge to L2, whereas dank sharding goals to scale Ethereum rollups to 100,000 TPS. That is attainable by making L2 knowledge plentiful and low-cost.
The principle aim of the roadmap is to additional scale back L2 fuel costs whereas growing throughput. Moreover, this improve will concentrate on L1 safety and cost enhancements.
Interoperability between L2
Interoperability between L2s is an idea launched by Optimism. An idea known as superchain introduces seamless communication between OP stack L2 chains.
Superchains intention to get rid of siled rollups and unify safety and governance throughout a number of L2s. This permits transactions to be moved between L2s by way of Cross-L2 Inboxes, bridging contracts, and standardized fault proofing.
It permits atomic cross-chain calls and permits the mixing of fuel tokens and liquidity throughout L2. For instance, OP stack L2s comparable to Base, Mode, Zora Community, and Frax Instrument can talk to kind a superchain.
Layer 3 options on the horizon
Layer 3 options are completely different from L2. Layer 2 is Ethereum’s general-purpose scaling answer, whereas L3 offers with scaling dApps. L3 handles custom-made use circumstances comparable to video games, enterprise apps, and privacy-focused rollups to cut back charges and scale transactions.
StarkNet’s L3 app chain, zkSync’s hyperchain, and Arbitrum Orbit are examples of L3 implementations. These options permit builders to leverage their very own rollups whereas inheriting L2 safety.


